Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects social interaction, communication, interests, and behavior. One aspect that often comes up in discussions about autism is the 'Autistic Stare,' a term that refers to a particular way individuals with autism might gaze or look at others or their surroundings. In this article, Connect n Care delves into the various facets of the 'Autistic Stare,' exploring what it is, its connection to autism, and the broader context of physical appearance and behaviors associated with autism.
What is an Autistic Gaze?
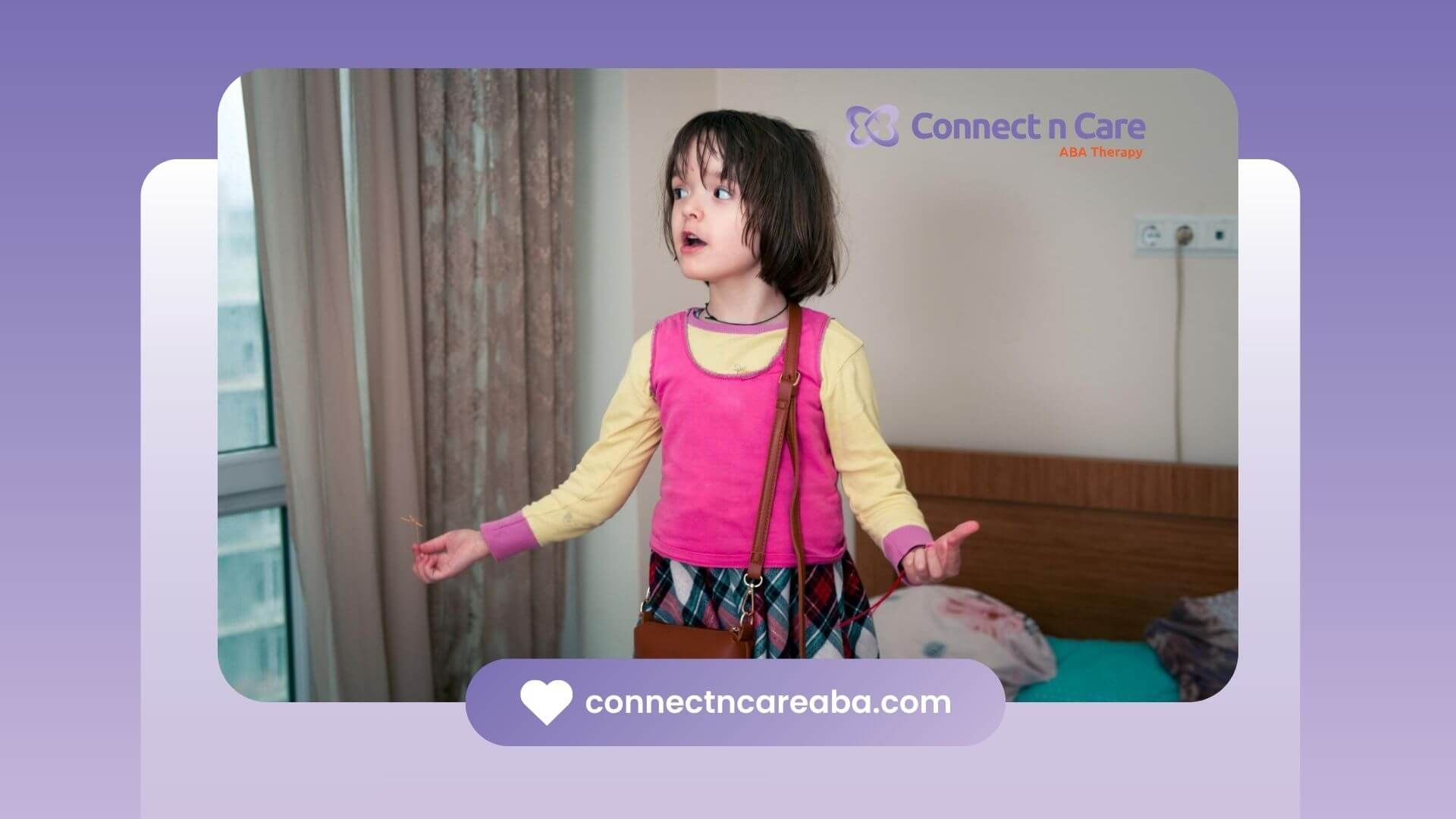
The term 'Autistic Gaze' often refers to a distinctive way of looking or not looking at others that is sometimes observed in individuals with autism. This gaze can be characterized by:
- Avoidance of Direct Eye Contact:
Some individuals with autism may find direct eye contact uncomfortable or overwhelming, leading to avoidance.
- Prolonged Staring:
Conversely, some might engage in prolonged staring, which can be misinterpreted by those not familiar with autism.
- Differences in Processing Visual Information:
The autistic gaze might also reflect differences in how individuals with autism process visual information, focusing on certain details others might overlook.
Is Staring a Form of Autism?
Staring in itself is not a form of autism, nor is it exclusive to individuals with autism. However, atypical eye contact, including staring, can be one of the many behaviors associated with autism. It's important to understand that autism is a spectrum, and behaviors vary widely among individuals. Staring alone, without other symptoms, is not sufficient to suggest a person has autism.
What Does 'Autism Eyes' Mean?
Autism Eyes' is a colloquial term that sometimes refers to the unique eye contact or gaze associated with individuals on the autism spectrum. This term can encompass:
- Unusual Eye Contact:
Either avoiding eye contact or engaging in intense staring.
- Focus on Specific Details:
Fixating on particular aspects of a person's face or eyes.
- Expressive Differences:
Sometimes, individuals with autism may express emotions differently through their eyes, which can be misread by others.
What are Signs of Autism in Physical Appearance?
Autism is primarily a neurological condition and does not have specific physical appearance traits. However, certain behaviors and movements might be more common in individuals with autism, such as:
- Repetitive Movements:
Such as hand-flapping, rocking, or spinning.
- Coordination Differences:
Some individuals might have unique gait patterns or motor skills.
- Facial Expressions:
There may be differences in how emotions are expressed facially.
What are the Facial Features of Autism Eyes?
While there are no definitive facial features unique to autism, some characteristics often discussed in the context of 'Autism Eyes' include:
- Intensity or Lack of Eye Contact:
Either a penetrating gaze or a tendency to look away.
- Focus on Mouths Instead of Eyes:
Some individuals with autism might focus on a person's mouth rather than their eyes when communicating.
- Blinking Patterns:
There might be differences in blinking frequency or pattern.
Is Staring a Form of Stimming?
Stimming, or self-stimulatory behavior, is a common aspect of autism, involving repetitive movements or noises. Staring can sometimes be a form of stimming. It may serve various functions, such as:
- Self-Regulation:
Helping to manage sensory overload or emotional distress.
- Focus and Concentration:
Aiding in focusing or coping with a busy environment.
- Sensory Exploration:
Engaging with the environment in a sensory-pleasing way.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 'Autistic Stare' and related concepts like 'Autism Eyes' reflect the diverse ways individuals with autism might interact with the world visually. It's crucial to approach these behaviors with understanding and awareness, recognizing the wide spectrum of autism and the unique experiences of each individual. By doing so, we foster a more inclusive and empathetic society.
At Connect n Care ABA, we’re committed to supporting every individual’s unique journey with autism through compassionate, tailored ABA therapy in North Carolina and Virginia.
Support your child’s visual and behavioral needs. Contact us today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the “autistic stare”?
The “autistic stare” refers to a behavior where individuals with autism may gaze without blinking or make intense eye contact. This is often due to sensory sensitivities, difficulty processing social cues, or being deeply focused on something. It is important to note that this behavior is not intended to be rude or disrespectful but is simply a characteristic of how some individuals with autism interact with the world.
Why do individuals with autism make prolonged eye contact?
People with autism may make prolonged eye contact or may seem to “stare” at others because they can have difficulty understanding or interpreting social cues. This behavior can stem from challenges in social communication, where making eye contact might feel uncomfortable or overwhelming, even though it may be misinterpreted as staring.
Is the “autistic stare” a sign of aggression?
No, the “autistic stare” is not a sign of aggression. For individuals with autism, prolonged or intense eye contact may be a way of processing information or managing sensory overload. It is often a sign of being absorbed in their thoughts, rather than an attempt to be confrontational or aggressive. Understanding this behavior is important for fostering better communication and social interactions.
SOURCES:
https://www.autismparentingmagazine.com/autism-stare/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34102517/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36416030/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10123036/
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychiatry/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1250763/full